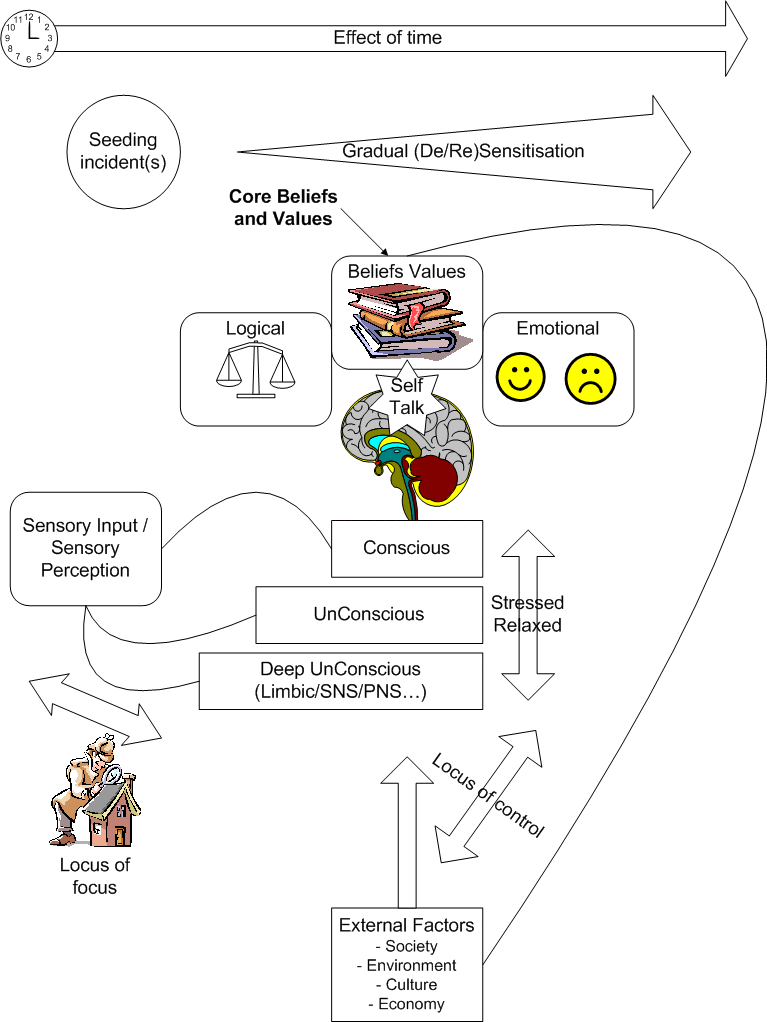
The world of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy takes the view that we are largely, but not exclusively, responsible for how we feel and act by the views we take of life events. CBT suggests that the beliefs we choose to hold about ourselves and the world around us substantially influence how we habitually choose to view events. Additionally, each time we respond to an event the same way we are reinforcing that conditioned response.
By understanding the interplay between thoughts (cognitions) and actions (behaviours) a large range of cognitive behavioural techniques have been developed that seek to facilitate rapid change. Many of these techniques are substantially more effective and less confrontational when implemented within hypnotherapy sessions and this gave rise to the concept of Cognitive Behavioural Hypnotherapy.
The objective of Cognitive Behavioural Hypnotherapy is to convert negative beliefs into more positive and effective beliefs, to gain control over negative thoughts and to change behavioural responses and habitual patterns.
Cognitive Behavioural Hypnotherapy based techniques are used as and when required or necessary during the therapeutic process. The approaches used will be discussed with you in the first session.,
Cognitive Behavioural thinking helps us all to understand and model how we function as emotive yet rational beings. This in its own right can help to facilitate change.
A brief history of cognitive behavioural therapy can be found here…
Research supporting Cognitive Behavioural Hypnotherapy
“A meta-analysis was performed on 18 studies in which a cognitive-behavioural therapy was compared with the same therapy supplemented by hypnosis. The results indicated that the addition of hypnosis substantially enhanced treatment outcome, so that the average client receiving cognitive-behavioural hypnotherapy showed greater improvement than at least 70% of clients receiving nonhypnotic treatment. […] These results were particularly striking because of the few procedural differences between the hypnotic and nonhypnotic treatments.” (Kirsch et al., 1996)
“We believe on the basis of our clinical experience that when behaviour therapy and hypnosis are used together, a synergistic effect results.” (Kroger & Fezler, 1976: 74).
